The Importance of Concurrency Control
Database concurrency control is the silent hero that protects data integrity when hundreds or thousands of users try to read and write data simultaneously. With DBDesigner’s collaborative modeling tools, teams can visually design schemas that remain conflict-free even under heavy transactional workloads.
“Over 72% of production outages in distributed systems stem from improper concurrency handling.” – 2024 Distributed Data Report
Why Concurrency Control Matters
- Prevents Data Corruption: Avoid lost updates, dirty reads, and inconsistent states
- Supports Scalability: Safely handle more users without sacrificing reliability
- Maintains Accuracy: Ensures every transaction sees valid, stable data
- Optimized Workflows: DBDesigner visualizes locking & isolation dependencies
Common Concurrency Issues
Visual design tools like DBDesigner help teams anticipate and avoid these problems:
- Dirty Reads: Reading uncommitted changes from another transaction
- Non-Repeatable Reads: Same query returns different results within the same transaction
- Phantom Reads: New rows appear between repeated queries
- Lost Updates: Concurrent writes overwrite each other without detection
Concurrency in Action: A Real Example
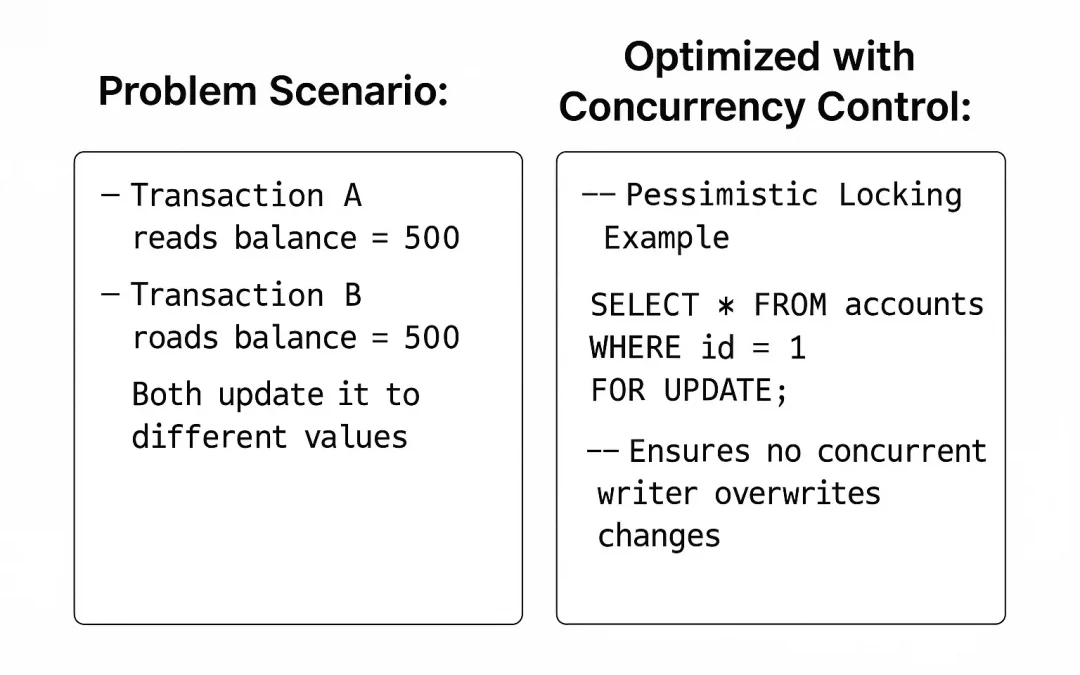
Problem Scenario: Two users update the same row at the same time.
-- Transaction A reads balance = 500
-- Transaction B reads balance = 500
-- Both update it to different values
Optimized with Concurrency Control:
-- Pessimistic Locking Example
SELECT * FROM accounts
WHERE id = 1
FOR UPDATE;
-- Ensures no concurrent writer overwrites changesBenefits
- Eliminates lost updates
- Ensures transactional accuracy
- Avoids race conditions in high-traffic systems
Concurrency Control Techniques
- Pessimistic Locking: Lock rows before reading them
- Optimistic Locking: Use version numbers to detect conflicts
- Timestamp Ordering: Allow natural ordering of concurrent operations
- Multiversion Concurrency Control (MVCC): Readers never block writers
Choosing Isolation Levels
Read Committed
- Prevents dirty reads
- Most common default level
Repeatable Read
- No non-repeatable reads
- MVCC performs especially well here
Serializable
- Highest integrity guarantee
- Simulates sequential transactions
Best Practices for Reliable Concurrency
- Design tables with clear primary keys and version fields
- Use short-lived transactions to reduce lock contention
- Leverage MVCC for read-heavy workloads
- Map isolation levels visually in DBDesigner’s ERD diagrams
Conclusion: Safeguard Your Data with Concurrency Control
Effective concurrency control ensures your database runs safely—even under extreme load. Modern teams rely on strong concurrency strategies to:
- Prevent data corruption
- Guarantee consistent transactional behavior
- Scale confidently with growing users
Start Building Safer Data Models
Design concurrency-friendly schemas using DBDesigner’s collaborative tools
For Enterprise Systems: Architect high-integrity, multi-user databases visually

Recent Comments