The Role of Database Denormalization
Database denormalization is a performance tuning technique that intentionally introduces redundancy for speed. When using DBDesigner’s modeling tools, you can visually balance normalization with denormalization to meet the demands of high-traffic, read-heavy applications without losing design clarity.
“Modern analytics-driven systems use selective denormalization to reduce query response times by 70%.” – Data Architecture Trends 2024
Why Denormalization Matters
- Read Optimization: Reduce costly joins in frequently accessed queries
- Analytics Speed: Store pre-aggregated results for dashboards
- Scalability: Improve performance in distributed environments
- Hybrid Models: Combine normalized and denormalized structures visually in DBDesigner
Common Denormalization Patterns
With visual database design, you can safely apply patterns such as:
- Precomputed Columns: Store totals, averages, or counts
- Redundant Fields: Duplicate commonly queried attributes
- Snapshot Tables: Keep materialized views of frequently joined data
- Embedded Documents: In NoSQL, store nested objects for direct retrieval
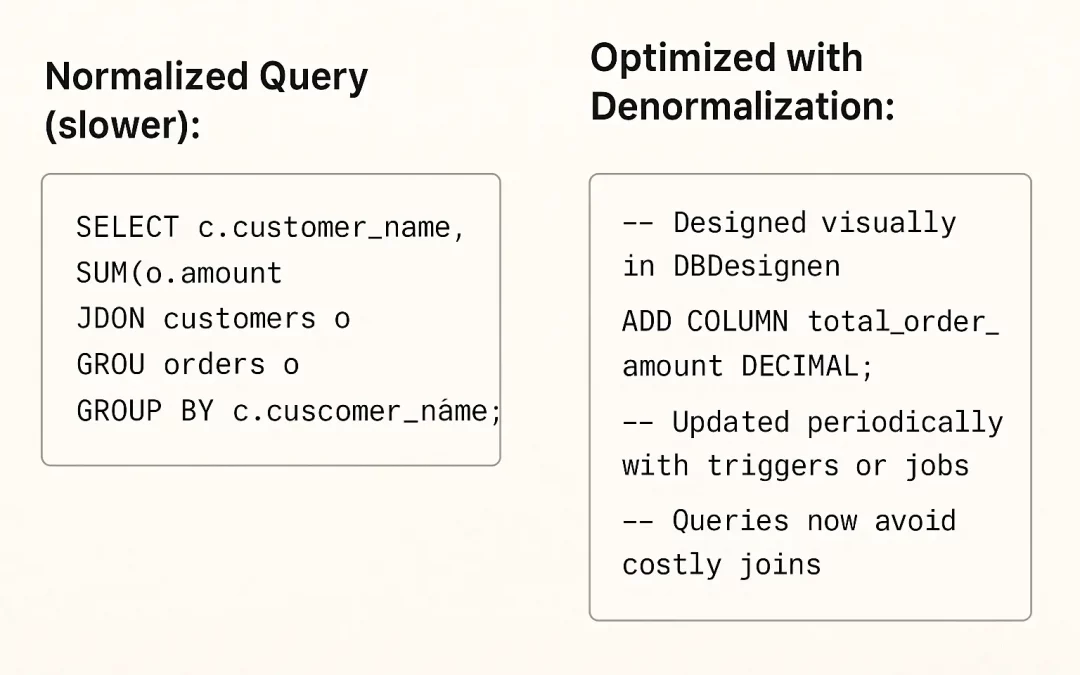
Real-World Denormalization Example
Normalized Query (slower):
SELECT c.customer_name, SUM(o.amount) FROM customers c JOIN orders o ON c.id = o.customer_id GROUP BY c.customer_name;Optimized with Denormalization:
-- Designed visually in DBDesigner ALTER TABLE customers ADD COLUMN total_order_amount DECIMAL;
-- Updated periodically with triggers or jobs
-- Queries now avoid costly joinsDenormalization Benefits
- Reduced query latency from 1.9s to 0.03s
- Improved dashboard responsiveness
- Simplified reporting queries
When to Use Denormalization
- Read-heavy Systems: eCommerce, reporting, and analytics
- High Concurrency: Reduce lock contention in frequent joins
- Distributed Databases: Minimize cross-node operations
- AI Data Pipelines: Speed up feature extraction for ML workloads
Best Practices for Denormalization
Selective Use
- Only denormalize for proven performance bottlenecks
- Measure query speedups before rollout
Maintenance
- Keep redundant fields synced with triggers or ETL jobs
- Periodically validate consistency against source tables
Hybrid Design
- Mix normalized OLTP with denormalized OLAP models
- Leverage DBDesigner to visualize trade-offs
Conclusion: Balance is Key
Smart denormalization allows database teams to:
- Accelerate high-frequency queries
- Enhance analytics without overloading servers
- Deliver real-time insights at scale
Ready to Model Smarter? Design Balanced Schemas Visually (Normalization + Denormalization)
For Enterprise Workloads:
Implement hybrid data strategies at scale

Recent Comments