Ensuring Integrity with Database Auditing
Database auditing is the silent guardian of data integrity. It records every change, access, and anomaly across your system, ensuring accountability and compliance. With DBDesigner’s collaborative tools, database architects can visually implement auditing structures that integrate seamlessly across platforms like PostgreSQL, MySQL, and SQL Server.
“Over 78% of enterprises in 2025 rely on database audit trails for compliance verification.” – Global Data Compliance Survey
Why Auditing Matters More Than Ever
- Data Accountability: Track who changed what and when
- Regulatory Compliance: Meet GDPR, HIPAA, and SOC 2 requirements
- Incident Analysis: Reconstruct historical data events
- Proactive Security: Detect unauthorized access in real-time
Core Components of Database Auditing
With visual schema design, you can plan a consistent auditing layer that supports:
- Audit Tables: Store historical actions and metadata
- Triggers: Automatically log changes without code repetition
- Change Logs: Maintain chronological modification records
- User Sessions: Capture login and query activity
- Retention Policies: Define how long audit data is preserved
Real-World Auditing in Action
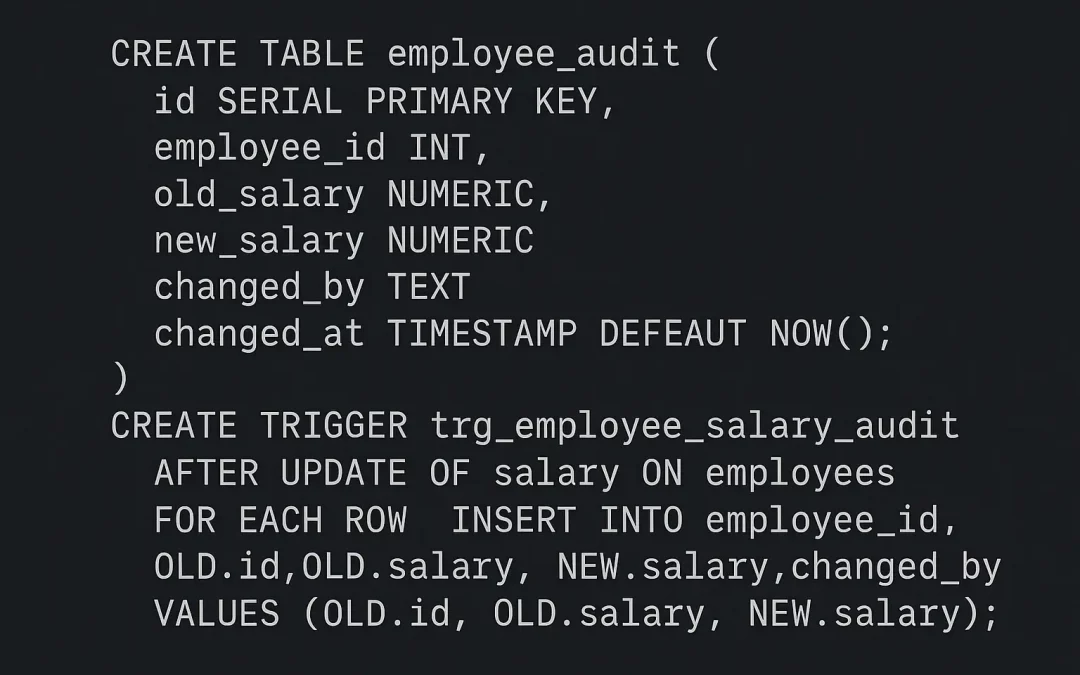
Example Audit Trigger:
CREATE TABLE employee_audit (
id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY,
employee_id INT,
old_salary NUMERIC,
new_salary NUMERIC,
changed_by TEXT,
changed_at TIMESTAMP DEFAULT NOW()
);
CREATE TRIGGER trg_employee_salary_audit
AFTER UPDATE OF salary ON employees
FOR EACH ROW
INSERT INTO employee_audit (employee_id, old_salary, new_salary, changed_by)
VALUES (OLD.id, OLD.salary, NEW.salary, SESSION_USER); Audit Benefits
- Detects unauthorized updates instantly
- Preserves a forensic data trail
- Improves team accountability
Advanced Auditing Techniques
- Row-Level Security (RLS): Enforce per-user data visibility
- Temporal Tables: Automatically store data history
- Immutable Logs: Use blockchain-like verification
- AI-driven Anomaly Detection: Identify unusual change patterns
Best Practices for Sustainable Auditing
Design
- Integrate auditing into ERD during early stages
- Keep audit tables separate from operational data
Performance
- Archive old audit data periodically
- Use partitions for high-volume audit tables
Compliance
- Encrypt audit logs at rest
- Restrict audit access to admins only
Conclusion: Audit for Trust & Transparency
Modern database ecosystems require more than speed—they demand traceability and trust.
By embedding auditing features visually in your schema design, you:
- Ensure regulatory compliance
- Boost data reliability
- Empower security and governance teams
Ready to Secure Your Data Workflows?
Design Auditing Structures Visually Today
(With automatic trigger generation and AI integrity checks)
For Enterprise-Grade Governance: Implement full compliance-ready audit systems

Recent Comments