The Power of Database Sharding
Database sharding is a scalability enabler that allows applications to handle millions of users without slowing down. With DBDesigner’s visual modeling, you can plan and simulate sharding strategies across major engines (PostgreSQL, MySQL, MongoDB, etc.)—all without writing manual partition logic.
“Sharded architectures improve read/write throughput by 300% in high-traffic systems according to 2024 Cloud Scaling Benchmark.” – Distributed Systems Review
Why Sharding Unlocks Scale
- Data Distribution: Split large datasets into smaller, manageable shards
- Load Balancing: Spread traffic evenly across nodes
- High Availability: Minimize single points of failure
- Global Reach: Deploy shards in multiple geographic regions
Common Sharding Strategies
Visual design with DBDesigner makes sharding patterns clear:
- Hash Sharding: Distribute records evenly using hash functions
- Range Sharding: Partition based on ranges (e.g., dates, IDs)
- Geographic Sharding: Assign data to regions for low latency
- Directory Sharding: Lookup-based mapping for flexible routing
Real-World Sharding Example
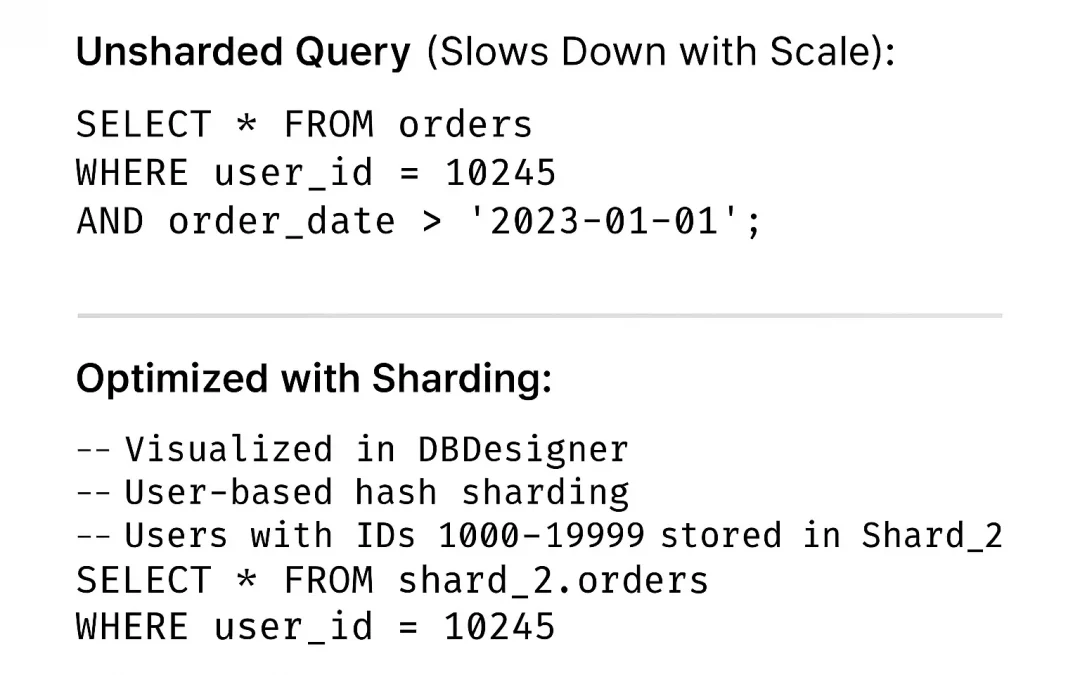
Unsharded Query (Slows Down with Scale):
SELECT * FROM orders
WHERE user_id = 10245
AND order_date > '2023-01-01';Optimized with Sharding:
-- Visualized in DBDesigner
-- User-based hash sharding
-- Users with IDs 10000–19999 stored in Shard_2
SELECT \* FROM shard\_2.orders
WHERE user\_id = 10245
AND order\_date > '2023-01-01';Shard Benefits
- Reduced query response time from 4.8s to 0.09s
- Enabled parallel reads/writes
- Improved fault isolation
Advanced Sharding Tactics
- Hybrid Sharding: Combine hash + range for complex workloads
- Dynamic Resharding: Rebalance automatically as data grows
- Shard-Aware Caching: Reduce cross-shard queries
- AI-Driven Modeling: DBDesigner’s AI suggests shard boundaries
Sharding Best Practices
Planning
- Align shard keys with query access patterns
- Estimate data growth rates per shard
Monitoring
- Detect hotspots (uneven shard usage)
- Track cross-shard joins for inefficiencies
Maintenance
- Automate resharding as clusters expand
- Ensure replication for durability
Conclusion: Shard for Growth
Modern engineering teams rely on database sharding to:
- Scale seamlessly as data explodes
- Maintain lightning-fast queries under heavy traffic
- Support globally distributed users
Ready to Scale Your Data?
Design Sharded Architectures Visually (With AI-powered shard key recommendations)
For Global-Scale Systems: Implement enterprise-grade sharding models

Recent Comments